Genetic Techniques
Wolbachia Project
What is it?
We are part of the Wolbachia Project national collaboration and outreach studying the bacterial endosymbiont Wolbachia pipientis.
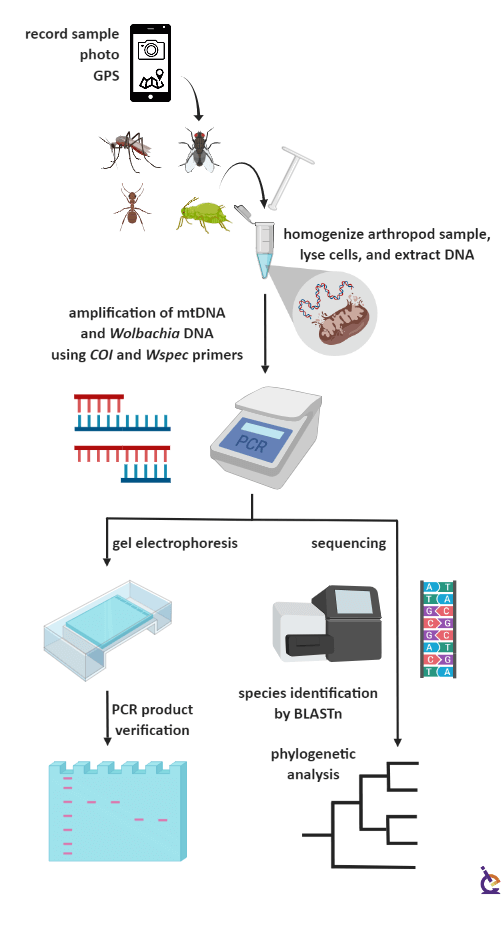
In the Wolbachia Project, students collect arthropods, preferably mosquitoes, and extract their DNA. A portion of the mitochondrial DNA is individually amplified and sequenced to identify the species of each collected insect. Then, students screen the DNA looking for a Wolbachia gene. Next, students use bioinformatics software to build phylogenetic trees of the insects and to determine genetic distance. Then, they match whether the strains of Wolbachia restrict to distinct phylogenetic branches.
A portion of this initiative is together administered by the National Science Foundation (NSF) and by Dr. Seth Bordenstein and team at Vanderbilt University.
What are Wolbachia?
Wolbachia are endosymbiont bacteria that infect 40–70% of all insects species (and some parasitic worms).
Why are Wolbachia important?
Wolbachia are a potential controlling agent against mosquitoes that transmit human viruses.
Wolbachia Project Report
x
Wolbachia Project Genetic Techniques
x
Laboratory Manual
x
Copyright Policy
The Wolbachia Project is made available under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-No Derivatives International License.
Contact [email protected] about adaptations.
Wolbachia Project Genetic Techniques Overview
Your content goes here. Edit or remove this text inline or in the module Content settings. You can also style every aspect of this content in the module Design settings and even apply custom CSS to this text in the module Advanced settings.
Wolbachia Project Genetic Techniques Flow Chart
Record Keeping
Common metric prefixes for molecular biology range from femto (10−15) to giga (109).
Lab Safety
The on-site Lab Safety training includes lab-specific hazards, location of safety equipment, evacuation routes, appropriate dress, use of personal protective equipment, professional behavior, proper organization, and correct disposal of lab materials. Here, students acknowledge and sign having completed all safety training at the beginning of the first class session. Lab safety is a component of the final course grade, and negligence can result in the offending student dropped from the course.
Electronic Devices
This laboratory has dedicated laptops for each student research group to access this website and other online resources. The laboratory has dedicated digital cameras and ink markers for labeling and taking images of tube contents and gels. No laboratory electronic devices should leave this laboratory because of contamination possibilities. Further, no personal electronic device use allowed inside this laboratory.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
This laboratory has available disposable lab coats and gloves of all sizes. If your PPE becomes contaminated with a biological agent or chemical, dispose of it in the available autoclave bags. This laboratory has available two sizes of lab safety glasses. Store clean PPE in your lab space cabinet. Return lab safety glasses to the lab manager after each lab session for sanitation and reuse. No exiting this laboratory while wearing this PPE because of contamination possibilities.
Biological Agents
This laboratory operates as a Biosafety Level 1 (BSL-1) environment. After collecting the arthropods, first freeze them overnight, and subsequently bring them to the lab. No living organisms or recombinant DNA used inside this laboratory space during this course. In addition, no living or non-living biological agents should leave this laboratory, including contaminated material.
Disposal of Tubes and Pipette Tips
This laboratory requires discarding all disposable material into the available labeled disposal box.
Reporting Biosafety Concerns
By email at [email protected]
By phone at 254-968-1647
Primary Literature
Your content goes here. Edit or remove this text inline or in the module Content settings. You can also style every aspect of this content in the module Design settings and even apply custom CSS to this text in the module Advanced settings.
Pipetting Techniques
Arthropod DNA extraction
Your content goes here. Edit or remove this text inline or in the module Content settings. You can also style every aspect of this content in the module Design settings and even apply custom CSS to this text in the module Advanced settings.
Amplification of DNA by PCR
Your content goes here. Edit or remove this text inline or in the module Content settings. You can also style every aspect of this content in the module Design settings and even apply custom CSS to this text in the module Advanced settings.
Gel Electrophoresis
Your content goes here. Edit or remove this text inline or in the module Content settings. You can also style every aspect of this content in the module Design settings and even apply custom CSS to this text in the module Advanced settings.
Arthropod Identification by DNA Barcoding
Your content goes here. Edit or remove this text inline or in the module Content settings. You can also style every aspect of this content in the module Design settings and even apply custom CSS to this text in the module Advanced settings.
Bioinformatics
Your content goes here. Edit or remove this text inline or in the module Content settings. You can also style every aspect of this content in the module Design settings and even apply custom CSS to this text in the module Advanced settings.